Explore In-Depth Dietary Guidelines for Achieving Peak Health
Enhance Your Wellbeing by Adhering to the Eatwell Guide
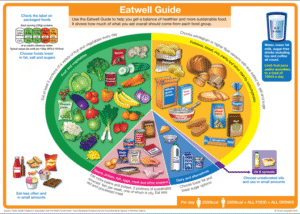
The Eatwell Guide serves as a crucial resource in nutritional guidance, presenting a clear visual representation that illustrates the optimal proportions of various food groups essential for creating a balanced diet. This vital guide stresses the necessity of consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, proteins, and healthy fats, while firmly recommending the reduction of foods high in sugar, salt, and saturated fats. By following the principles outlined in the Eatwell Guide, individuals can ensure they are obtaining the essential nutrients required to support their overall health and wellbeing.
If you are an auditory learner, feel free to click below to listen!
Applying this knowledge in your everyday life is remarkably simple. For instance, aim to fill half of your plate with fruits and vegetables, which not only meets the recommended intake but also provides vital vitamins and minerals. The guide encourages a variety of food choices, highlighting that different foods offer distinct health benefits. For example, legumes such as lentils and chickpeas are outstanding sources of protein and dietary fibre. Furthermore, oily fish is particularly esteemed for its rich content of omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential for maintaining excellent heart health.
While the Eatwell Guide provides a strong framework, it also emphasises the importance of personalised dietary approaches. Individual health issues, age, and activity levels significantly influence specific nutritional requirements. Additionally, it is essential to consider cultural preferences when planning meals, as diverse culinary traditions can greatly enhance the dining experience, making meals more enjoyable and satisfying.
Grasping Recommended Daily Allowances for Optimal Nutritional Equilibrium
Recommended Daily Allowances (RDAs) are established to ensure that the nutritional needs of the population are adequately met. These guidelines outline suggested daily intake levels for crucial nutrients that are essential for sustaining good health. RDAs differ based on various factors, including age, sex, and specific life stages such as pregnancy or lactation. For instance, adult men and women have distinct requirements for iron, with women typically needing higher levels due to losses incurred during menstruation.
Understanding the significance of RDAs is vital for those seeking to improve their nutrient intake through a well-balanced diet. If your iron intake is insufficient, consider incorporating iron-rich foods into your meals or exploring the option of a supplement to help meet your needs.
Foods such as red meat, poultry, and fortified cereals are excellent sources of iron. Individuals following vegetarian or vegan diets may turn to legumes, nuts, and seeds as alternative sources of protein. This knowledge is crucial for effective personal health management and for preventing nutrient deficiencies.
Keeping track of your nutrient intake against the RDAs can be particularly important for various demographic groups. Athletes may have increased protein requirements, while older adults might need more calcium and vitamin D to maintain robust bones. When planning meals or considering supplements, it is vital to evaluate individual needs to ensure compliance with recommended guidelines.
Recognising and Mitigating Common Nutrient Deficiencies
Despite the guidance provided by the Eatwell Guide and RDAs, numerous individuals encounter prevalent nutrient deficiencies. For example, a vitamin D deficiency is commonly seen within the population, exacerbated by limited sunlight exposure during the winter months. The lack of adequate sun exposure results in many individuals not producing sufficient vitamin D naturally, prompting recommendations for supplementation to maintain adequate levels.
Moreover, iron deficiency remains a significant concern, particularly among women and those adhering to vegetarian diets. Symptoms such as fatigue and weakness may indicate low iron levels. In these situations, dietary modifications and supplements can play a central role in addressing deficiencies and promoting a more balanced diet. Integrating iron-rich foods like lentils, beans, and fortified cereals into your daily meals, along with vitamin C-rich fruits, can greatly enhance iron absorption and effectively combat iron deficiency.
Furthermore, folate deficiencies are particularly common among women of childbearing age. Folate is crucial for DNA synthesis and repair, making it especially important during pregnancy to prevent neural tube defects. Consuming fortified foods and supplements can help individuals meet their folate needs when adequate levels cannot be achieved through diet alone.
Essential Nutrients and Their Dietary Sources for Improved Health
Maximising Your Vitamin D Intake Through a Comprehensive Diet
The significance of vitamin D for promoting bone health and supporting immune function cannot be overstated. In regions where sunlight exposure is limited for extended periods, identifying sufficient sources of vitamin D becomes crucial. The primary dietary sources include oily fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, which are not only rich in vitamin D but also provide the body with essential omega-3 fatty acids.
Additionally, fortified foods play a key role in enhancing vitamin D intake; options include certain dairy products and breakfast cereals. Despite these sources, many individuals struggle to obtain adequate vitamin D solely from their diet. Therefore, particularly during the winter months, supplements become an essential resource for maintaining optimal levels. Public Health England advises a daily vitamin D supplement of 10 micrograms, especially for individuals with limited sunlight exposure.
Certain populations are at a heightened risk of vitamin D deficiency, including older adults, individuals with darker skin, and those who are housebound. These groups should be particularly vigilant about monitoring their vitamin D status and may benefit from regular screening and supplementation, as advised by healthcare professionals, to ensure optimal health outcomes.
Identifying Rich Sources of Iron for Your Diet
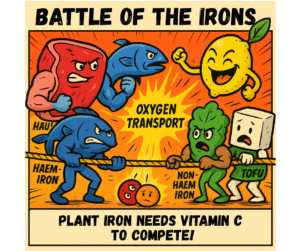
Iron is a vital mineral essential for the production of haemoglobin, which facilitates oxygen transport in the bloodstream. The primary sources of iron include red meat, poultry, and fish. However, for those adhering to vegetarian or vegan diets, animal-based iron sources are not an option. In these instances, plant-based sources such as lentils, beans, tofu, and fortified cereals become indispensable. Regularly incorporating these foods can help sustain adequate iron levels and prevent deficiencies.
To enhance the absorption of non-haem iron found in plant foods, pairing iron-rich meals with sources of vitamin C is highly beneficial.
This combination can significantly improve iron uptake within the body. For example, a salad containing chickpeas, bell peppers, tomatoes, and a squeeze of lemon can be particularly effective. This not only maximises iron absorption but also offers a nutritious and enjoyable meal.
Addressing iron deficiency is crucial, especially for certain demographics. Women of childbearing age are particularly at risk due to menstruation and pregnancy. Individuals experiencing symptoms such as fatigue, dizziness, or shortness of breath should consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and treatment. A healthcare provider can assess iron levels and recommend appropriate supplementation strategies to restore balance and support overall health.
Many people associate consuming iron-rich foods with traditional meals such as a hearty beef stew or a classic shepherd's pie. Highlighting these dishes in meal planning can effectively maintain iron levels while allowing for enjoyable flavours that resonate with cultural preferences, ultimately enhancing meal satisfaction.
Incorporating Omega-3 Fatty Acids into Your Daily Nutrition
Omega-3 fatty acids are widely recognised for their numerous advantages for heart health, but their significance extends beyond cardiovascular benefits to encompass cognitive function and reduced inflammation. Oily fish, such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, serve as the primary dietary sources of omega-3 fatty acids. Including these fish in your diet at least twice weekly aligns with health recommendations while providing a delicious method to enhance your nutrient intake.
For those who do not regularly consume fish, alternative sources of omega-3 fatty acids are readily available. Flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts offer excellent plant-based options. Additionally, certain fortified foods, such as specific brands of eggs and dairy products, also contain omega-3s. When aiming to increase omega-3 intake, it is essential to balance it with omega-6 fatty acids, commonly found in many processed foods. Achieving a favourable omega-3 to omega-6 ratio is crucial for maintaining optimal health. 
Incorporating omega-3-rich foods into your daily meals can be both enjoyable and creative. Consider starting your day with a smoothie that includes flaxseeds, or crafting a vibrant salad topped with walnuts. Alternatively, a simple dish of grilled salmon served alongside roasted vegetables can be both satisfying and nutrient-rich, making a positive contribution to your overall health.
For individuals who find it challenging to meet their omega-3 requirements through diet alone, supplements are widely available.
Both fish oil and algal oil supplements are popular choices. Algal oil is a suitable option for those adhering to a vegan lifestyle. Consulting with a healthcare provider is essential, as they can assist in determining the appropriate type and dosage based on your health needs and dietary preferences.
Strategic Approaches to Supplementation for Enhanced Health
Identifying the Optimal Time to Introduce Supplements into Your Diet
Determining the best time to consider supplements is vital for maintaining a balanced diet. Certain nutrients may be lacking due to dietary habits or life circumstances. For example, during the winter months, limited sunlight can lead to insufficient vitamin D production in the skin. In such instances, supplementation becomes a practical option to help prevent deficiency.
Individuals with specific dietary restrictions, such as vegetarians or vegans, may also find it challenging to meet their nutrient needs through food alone. For instance, vitamin B12, primarily found in animal products, can become deficient for those following a plant-based diet, necessitating supplementation. Similarly, iron levels may be inadequate for individuals who do not consume meat, making it crucial to consider iron-rich supplements.
Individuals with malabsorption issues or chronic health conditions may require a personalised supplementation plan. This tailored approach effectively addresses their unique health challenges. For example, individuals with coeliac disease or Crohn's disease often struggle to absorb nutrients; they may benefit from specific supplements to help restore balance and enhance their overall health.
While supplements can effectively bridge dietary gaps, they should not replace a well-rounded diet. It's critical to approach supplementation thoughtfully and with care. Any additions to your routine should align with your nutritional needs and be backed by scientific evidence. Consulting with a healthcare provider can provide personalised recommendations and help monitor nutrient levels for the best health outcomes.
Ensuring Quality When Selecting Supplements
Understanding ingredient sourcing is crucial in your pursuit of high-quality supplements. Opt for products that utilise bioavailable forms of vitamins and minerals, which are more readily absorbed and utilised by the body. For example, magnesium citrate is a more absorbable form of magnesium compared to magnesium oxide.
It is vital to scrutinise labels for potential allergens and unnecessary fillers. Transparency in labelling not only fosters informed consumer choices but also safeguards against adverse reactions. Brands that provide clear information about their sourcing, production processes, and testing protocols are generally more trustworthy and reputable.
In an era where the supplement market is saturated with options, conducting thorough research before making a purchase can yield beneficial results. Consumer reviews, professional endorsements, and scientific studies can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of specific brands and products. This diligence ensures that the supplements you choose genuinely support your health goals and align with a balanced diet.
Optimising Dosage and Timing for Maximum Nutritional Benefit
Understanding the appropriate dosage and timing for supplements is crucial for maximising their benefits. Specific guidelines exist for various nutrients, with healthcare providers commonly recommending dosages tailored to individual needs. For example, the standard dosage for vitamin D supplementation is generally around 10 micrograms daily for most adults, especially during the winter months when sunlight exposure is limited.
Timing also plays a significant role that can greatly influence nutrient absorption. Certain supplements, such as fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K), are best taken with meals containing fat to enhance their absorption and utilisation. Conversely, water-soluble vitamins, such as vitamin C and B vitamins, can be consumed on an empty stomach for optimal absorption.
Moreover, some minerals can negatively interact with each other when taken simultaneously. For instance, calcium can inhibit iron absorption when consumed together, so spacing these supplements apart by a few hours can be beneficial. Following the guidance of healthcare professionals regarding the timing of supplements can help avoid potential interactions and improve overall nutrient intake.
For individuals managing specific health conditions, customised strategies may be required. Consulting with a registered dietitian or healthcare provider can offer insights into the best practices for supplement timing and dosage tailored to individual health scenarios, ensuring a more effective approach to pairing supplements with a balanced diet.
Highlighting Common Nutrient Deficiencies for Increased Awareness
Addressing prevalent nutrient deficiencies is essential for maintaining optimal health, especially when specific dietary habits may elevate the risk of deficiencies. One widespread deficiency is iron, particularly among women of reproductive age. Symptoms often manifest as fatigue or reduced energy levels, underscoring the importance of ensuring adequate iron intake through diet or supplementation.
Another area of concern is vitamin B12 deficiency, especially for those following plant-based diets, as this vitamin is primarily sourced from animal products. A lack of B12 can lead to neurological issues and anaemia, highlighting the necessity of monitoring levels and considering fortified foods or supplements to maintain adequate intake.
Folate, essential for cell division and the synthesis of DNA, is particularly crucial for women planning to conceive. Deficiencies in folate can lead to serious complications during pregnancy, making supplementation vital for women in this demographic to ensure healthy outcomes.
To combat these deficiencies, individuals should prioritise nutrient-dense foods in their diets. For instance, consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains can effectively address many nutrient shortfalls. If dietary adjustments prove insufficient, supplements can serve as a targeted approach to restoring nutrient levels. Consulting with a healthcare provider is advisable to assess individual needs and determine an appropriate supplement regimen tailored to effectively combat specific deficiencies.
The Vital Role of Healthcare Providers in Supplementation Guidance
Before embarking on any supplementation journey, consulting with a healthcare provider is essential to tailor choices to individual health needs. A registered dietitian or general practitioner can offer personalised recommendations based on dietary patterns, health goals, and lifestyle factors. They can also evaluate existing health conditions that may necessitate the use of specific supplements.
A comprehensive assessment may involve blood tests to evaluate existing nutrient levels, especially for those suspected of deficiencies. This data-driven approach ensures that supplementation is not only safe but also effective in addressing individual needs and optimising health.
It is crucial to view supplementation as a complement to, rather than a substitute for, a balanced diet. Healthcare providers can guide individuals in making dietary modifications, assisting them in incorporating foods that naturally support optimal nutrient intake. This dual approach, combining a robust diet with well-chosen supplements, can optimise health outcomes and foster a holistic approach to overall wellbeing.
Maintaining open communication with healthcare providers regarding any side effects or concerns related to supplements is equally important. Adjustments to dosage or type may be necessary based on individual responses and changes in health status over time, ensuring a tailored approach to nutritional supplementation.
Targeted Supplements for Specific Health Conditions
Effective Strategies for Managing Seasonal Affective Disorder
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) presents unique challenges for many individuals, particularly during winter months when daylight hours are significantly reduced. One effective strategy for managing SAD involves vitamin D supplementation. Research suggests that maintaining adequate levels of vitamin D can enhance mood and overall mental well-being, making it a critical consideration for individuals affected by SAD.
Since sunlight is a primary source of vitamin D, reduced exposure during the winter months can lead to significant deficiencies. Many individuals experience symptoms such as fatigue, low energy, and irritability, all of which may be alleviated through appropriate supplementation. Public Health England recommends that individuals consider taking a daily supplement of 10 micrograms from October to March to help effectively mitigate these effects.
Alongside supplementation, incorporating regular physical activity and maintaining a balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids can further support mood regulation. Foods such as fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts can enhance brain function and emotional health, positively contributing to overall wellbeing during the winter months.
Professional support and counselling may also play a vital role in managing SAD. Combining dietary approaches and supplementation with therapeutic techniques can create a comprehensive strategy for individuals seeking relief from seasonal mood fluctuations, leading to improved mental health outcomes.
Effective Management of Anaemia Through Nutritional Strategies
Anaemia is a prevalent condition, particularly affecting women, children, and individuals with specific dietary restrictions. Iron deficiency anaemia occurs when there is insufficient iron to produce adequate haemoglobin in the blood. Symptoms may include fatigue, weakness, and pale skin, highlighting the importance of promptly addressing this deficiency through dietary modifications and supplementation.
For at-risk individuals, increasing the intake of iron-rich foods should be a primary focus. Red meat, poultry, fish, lentils, and fortified cereals are all rich in iron. However, when dietary changes fail to provide adequate iron, iron supplements may become necessary. These supplements come in various forms, including ferrous sulfate, which is commonly recommended due to its effectiveness in addressing deficiency.
Individuals with anaemia must collaborate closely with healthcare professionals to monitor their iron levels and adjust their supplementation as needed. Regular blood tests can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of dietary changes and supplements, ensuring that individuals are progressing towards recovery and optimal health.
Additionally, being aware of factors that inhibit iron absorption can help optimise dietary choices. For example, consuming calcium-rich foods or beverages alongside iron-rich meals can hinder absorption. Therefore, timing these foods appropriately can enhance overall iron intake and prevent deficiencies.
Promoting Bone Health in Older Adults through Nutrition
Maintaining optimal bone health is a significant concern for older adults, particularly as the risk of osteoporosis increases with age. Both calcium and vitamin D are essential for sustaining bone density and health. Given the dietary limitations often observed in older populations, such as reduced dairy consumption or limited sun exposure, the need for effective supplementation becomes critical.
Vitamin D plays a pivotal role in calcium absorption, and without adequate levels, bone health can deteriorate. Older adults should consider taking vitamin D supplements, especially during the winter months when sun exposure is limited. Furthermore, incorporating calcium-rich foods like milk, cheese, and leafy green vegetables into their diets can further strengthen bone health and help prevent related issues.
Regular physical activity, particularly weight-bearing exercises, is also crucial for maintaining bone strength. Activities such as walking, dancing, or strength training can help enhance bone density and overall mobility, allowing older adults to maintain independence and quality of life as they age gracefully.
Healthcare providers play an essential role in evaluating bone health and recommending appropriate supplementation. Regular screenings for bone density can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of dietary and supplement strategies, ensuring that older adults maintain strong bones and overall health as they age.
Strategies for Combating Vitamin D Deficiency in Vulnerable Populations
Vitamin D deficiency is prevalent among individuals with limited sunlight exposure, particularly during the winter months. To address this, public health guidance recommends that everyone consider taking a daily vitamin D supplement. This guidance is especially important for those at a higher risk, including older adults, individuals with darker skin, and those who are housebound.
Incorporating vitamin D-rich foods into the diet is essential, but many individuals find it challenging to achieve sufficient levels through diet alone. Oily fish, fortified dairy products, and egg yolks are excellent sources; however, they may not suffice for everyone, particularly in regions with limited sunlight exposure.
Monitoring vitamin D status through regular blood tests can help individuals better understand their needs and adjust their supplementation accordingly. It is vital to adhere to recommended dosages and consult with healthcare professionals when making adjustments to supplementation strategies, ensuring optimal health outcomes.
Raising awareness about vitamin D and its importance can empower individuals to take proactive measures in managing their health. By combining dietary approaches, lifestyle modifications, and supplementation, individuals can effectively combat vitamin D deficiency and enhance their overall wellbeing, paving the way for a healthier future.
Effectively Managing Iodine Deficiency
Iodine is an essential trace element that plays a critical role in thyroid function and overall metabolic health. Nevertheless, iodine deficiency is frequently overlooked, as dietary habits may not prioritise iodine-rich foods. Familiar sources of iodine include fish, dairy products, and iodised salt; however, many individuals do not consume sufficient amounts to meet their needs.
The ramifications of iodine deficiency can be significant, potentially leading to thyroid dysfunction and related health issues. Pregnant women are particularly at risk, as iodine is crucial for fetal development. Raising awareness about iodine intake is vital.
Supplements should be considered, especially for vulnerable populations at risk of iodine deficiency.
Iodine supplementation is often recommended for those on strict vegetarian or vegan diets, as plant-based foods typically contain less iodine. Sea vegetables, such as seaweed, can enhance iodine intake; however, proper sourcing and preparation are crucial to ensure they are safe and effective for consumption.
Consulting with healthcare providers can help individuals assess their iodine needs, particularly if they face a risk of deficiency. Regular monitoring and dietary adjustments can support thyroid health and overall wellbeing, ensuring individuals maintain optimal iodine levels, which are crucial for good health.
Understanding the Regulatory Framework Governing Dietary Supplements
The Role of the Food Standards Agency in Regulating Supplements
The Food Standards Agency (FSA) plays a critical role in overseeing food safety and dietary supplements within the UK. Its primary aim is to protect public health and consumer interests. It achieves this by ensuring that all food products, including dietary supplements, comply with stringent standards for safety and quality. The FSA establishes guidelines that manufacturers must follow, including accurate labelling, ingredient transparency, and safety evaluations.
Understanding the regulatory framework empowers consumers to make informed choices regarding the supplements they purchase. It is essential to opt for products that comply with FSA regulations, as these items are more likely to be of high quality and safe for consumption, thereby enhancing confidence in their effectiveness.
In addition to regulating supplements, the FSA provides guidance on nutrition and health claims made by supplement manufacturers. Claims must be substantiated by scientific evidence to prevent exaggerated or unfounded statements from misleading consumers about a product's benefits.
Staying informed about the regulatory landscape enables consumers to make educated dietary choices. Keeping abreast of FSA guidelines helps you select safe and effective supplements, supporting your health journey and overall wellness.
Essential Labelling Requirements for Dietary Supplements
Labelling is critical for ensuring consumer safety and informed decision-making regarding dietary supplements. All supplement labels must adhere to strict FDA regulations, detailing ingredients, dosage instructions, and potential allergens. This transparency is vital for consumers to comprehend what they are consuming and to avoid adverse reactions.
In recent years, there have been calls for more stringent labelling standards as the supplement market evolves. Consumers should read labels meticulously and seek certifications that affirm product quality and safety, promoting accountability in the supplement industry.
Labels should specify proper storage instructions for supplements and include expiry dates. They must also list health claims backed by scientific evidence. This information not only aids consumers in making informed choices but also bolsters the overall integrity of the supplement industry.
Understanding labelling requirements empowers consumers to navigate the extensive array of products available on the market with confidence. By being diligent about reading labels and seeking reputable brands, individuals can ensure they are making safe and effective choices that align with their health objectives.
Reporting Adverse Reactions to Supplements for Enhanced Safety
Consumers possess the right to report any adverse reactions they may experience from supplements. The Yellow Card scheme, managed by the Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA), allows individuals to report any side effects or safety concerns associated with dietary supplements. This system is crucial for monitoring the safety of supplements in the market and ensuring consumer protection.
Reporting adverse reactions is essential for the ongoing evaluation of supplement safety. The information collected through the Yellow Card scheme enables regulatory agencies to identify trends and potential issues, allowing for timely interventions when necessary. This transparency fosters consumer confidence in the supplement industry and encourages manufacturers to prioritise safety and quality in their products.
Individuals who experience adverse reactions are urged to report their experiences, regardless of the severity of the response. This collective information helps provide a broader understanding of supplement safety, potentially leading to stronger regulations and safety measures that better protect consumers.
Educating consumers about the significance of reporting adverse reactions empowers them to actively participate in their health management. By engaging in this process, individuals can help ensure that dietary supplements are safe and beneficial for everyone, enhancing the overall integrity of the industry.
Incorporating Supplements into Your Meal Planning for Enhanced Nutrition
Effortlessly Adding Supplements to Your Breakfast Routine
Integrating supplements into your breakfast routine can be a strategic way to kick-start your day healthily. Many individuals opt for fortified breakfast cereals, which present an excellent opportunity to add essential nutrients, such as vitamin D and iron, to your morning meal. Taking a vitamin D supplement alongside fortified cereal can enhance absorption, maximising the benefits of both the meal and the supplement.
A balanced breakfast sets the tone for the day. Adding nutrient-dense ingredients can significantly boost your overall nutrient intake. Fruits like berries or bananas contribute extra vitamins and minerals. A side of yoghurt provides probiotics that support your gut microbiome and digestive health. Including healthy fats such as a handful of nuts or seeds adds texture and flavour while helping you feel full and supporting your overall wellbeing. This type of breakfast nourishes your body and fosters a healthy routine, encouraging mindful eating and setting a positive tone for the rest of the day.
To optimise the benefits of your breakfast, aim for variety. Experiment with different combinations of cereals, fruits, and supplements to discover what works best for you. This flexibility can make breakfast enjoyable while helping you meet your dietary needs effectively and reinforcing positive habits.
Strategic Lunchtime Approaches for Supplement Integration
Lunchtime presents an excellent opportunity to complement your meals with targeted supplements. Many individuals find that incorporating omega-3-rich foods, such as salmon salad or a tuna sandwich, can enhance nutrient absorption, particularly when paired with a high-quality fish oil supplement to achieve adequate levels.
Furthermore, lunchtime is an ideal time to incorporate additional vitamins and minerals that may be lacking in your diet. For example, a mixed vegetable stir-fry paired with tofu or chicken provides an opportunity to add calcium and vitamin D supplements, especially for those at risk of deficiencies due to dietary restrictions.
As with breakfast, variety plays a key role during lunch. Exploring different cuisines can introduce new flavours while still focusing on nutrient density. Consider Mediterranean-style meals featuring chickpeas, olives, and whole grains, which can support overall health while allowing for the addition of necessary supplements to enhance nutritional intake.
Maintaining a mindful approach to lunchtime can help reinforce healthy eating habits. By actively integrating supplements into this meal, individuals can take proactive steps to ensure they are meeting their dietary goals and effectively supporting their overall health.
Evening Meals: Reinforcing Nutrient Intake with Strategic Supplementation
Evening meals provide an excellent opportunity to enhance your nutrient intake while enjoying quality time with family or friends. Incorporating omega-3 supplements with dinner can be particularly advantageous for heart health. Pairing a dish of grilled mackerel with a side of roasted vegetables not only delivers essential nutrients but also facilitates optimal absorption of both dietary and supplemental omega-3s, thus positively contributing to cardiovascular health.
Another effective strategy is to consider calcium and vitamin D supplements, especially for those at risk of osteoporosis. A hearty serving of leafy greens paired with a protein source like chicken or legumes can create a balanced meal that supports bone health and overall wellbeing.
Mindful meal planning can enhance nutrient intake while also fostering enjoyment in eating. Preparing meals that celebrate the fresh produce available can inspire creativity and ensure a wide variety of vitamins and minerals are included in your diet, making each meal not only nourishing but also delicious.
As the day winds down, taking a moment to reflect on your meals can reinforce positive dietary habits. By strategically incorporating supplements into your evening routine, you can effectively support your health and wellbeing, promoting a holistic approach to nutrition.
Frequently Asked Questions about Supplements
What benefits can dietary supplements provide in a balanced diet?
Utilising supplements can effectively bridge nutritional gaps, ensuring adequate intake of essential vitamins and minerals. They can support overall health, enhance nutrient absorption, and address specific deficiencies individuals may encounter due to their dietary habits or health conditions.
When should I consider adding supplements to my diet?
Consider taking supplements if you have dietary restrictions, low nutrient intake, or specific health conditions that may impede your nutrient absorption. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help you determine your individual needs and the most effective approach to supplementation.
How do I select the right supplements for my specific health needs?
Choose supplements that are certified for quality, contain bioavailable forms of nutrients, and avoid unnecessary fillers. Reading labels and conducting research on brands can also guide your choices, ensuring you select products that align with your health goals.
Is it safe to take supplements daily?
Many supplements are safe for daily use when taken as directed. However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications that may interact with supplements.
Can I obtain all my nutrients solely from food?
While a well-balanced diet can provide most nutrients, some individuals may require supplements to address specific deficiencies or dietary restrictions that limit their nutrient intake.
What are the most common nutrient deficiencies reported?
Common nutrient deficiencies include vitamin D, iron, and folate. These deficiencies can often be effectively resolved through dietary changes and supplementation, supporting overall health and wellbeing.
How can I determine if I need a supplement?
Consulting with a healthcare provider can help assess your nutrient levels. Blood tests can reveal nutritional deficiencies and guide your supplement choices to meet your health needs effectively.
Are there risks associated with taking supplements?
Yes, excessive intake of certain supplements can lead to toxicity or adverse effects. Following recommended dosages and consulting with a healthcare provider is crucial to mitigate potential risks associated with supplementation.
What foods are particularly rich in iron?
Iron-rich foods include red meat, poultry, fish, lentils, beans, and fortified cereals. Pairing these foods with sources of vitamin C can significantly enhance absorption, promoting better iron status.
How does vitamin D contribute to overall health?
Vitamin D is crucial for maintaining bone health, supporting immune function, and regulating mood. It aids the body in absorbing calcium and may lower the risk of certain diseases, highlighting its importance in sustaining overall health.
Connect with us on Facebook!
The Article: How to Pair Supplements with a Balanced Diet appeared first on https://janestevensnutrition.com
The Article: Pairing Supplements with a Balanced Diet: A Guide appeared first on https://janestevens.net
The Article Supplements and a Balanced Diet: Your Essential Guide Was Found On https://limitsofstrategy.com